Body odor is a natural part of human biology, yet it remains a topic of curiosity and sometimes concern. While many assume sweat is the primary culprit, the truth is more complex. Understanding the real causes of body odor can help in managing and reducing unwanted scents effectively.
The Science Behind Body Odor
-
Sweat and Its Role
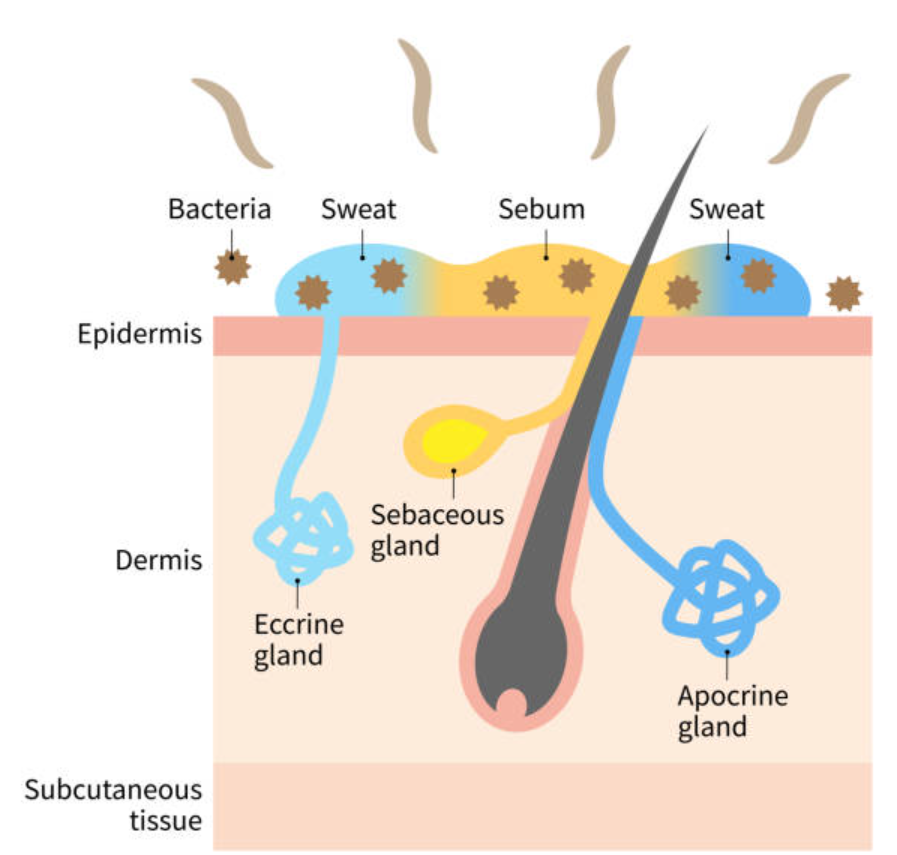
Sweat itself is nearly odorless. The human body has two main types of sweat glands:- Eccrine glands: Found all over the body, these produce a watery, salt-based sweat primarily to regulate temperature.
- Apocrine glands: Located in areas like the armpits and groin, these glands release a thicker sweat containing proteins and lipids, which become a food source for bacteria.
-
Bacterial Activity
- The real source of body odor is bacteria that break down the sweat from apocrine glands, producing compounds like isovaleric acid and thioalcohols, which have strong smells.
- Different types of bacteria contribute to variations in individual body odors.
-
Diet and Body Odor
- Certain foods, such as garlic, onions, spicy dishes, and alcohol, can alter body odor by affecting sweat composition.
- High-protein diets may lead to an increase in ammonia-related odors due to protein metabolism.
-
Hormonal and Genetic Influences
- Puberty triggers increased activity in apocrine glands, leading to stronger body odors.
- Genetics play a role in how intensely a person’s body odor develops, including variations in sweat composition.
-
Medical Conditions and Lifestyle Factors
- Conditions like hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating) or trimethylaminuria (a metabolic disorder causing a fish-like odor) can impact body scent.
- Stress-induced sweating tends to smell stronger due to higher activity of apocrine glands.
How to Manage and Reduce Body Odor
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Regular showering with antibacterial soap can help control bacteria.
- Use Natural or Clinical Deodorants: These can neutralize odors or reduce bacterial growth.
- Wear Breathable Fabrics: Cotton and moisture-wicking materials help reduce sweat buildup.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking water helps regulate metabolism and dilute sweat odors.
- Monitor Diet: Reducing strong-smelling foods may improve natural body scent.
Body odor is a complex interplay between sweat, bacteria, and individual factors. By understanding its origins, we can better manage and embrace this natural bodily function.

Leave a Reply